Using with MS Visual Studio Code
Microsoft Visual Studio Code is a free (as in “free beer”) and Open Source code editor for Windows, Linux and Mac.
Software involved
Installation
Install VS Code, extensions and tools
Navigate to project folder and create configuration as described below
Open workspace. If vscode is in your system path you can do this:
code .
Configuration
Please make sure you have critical environment variables set globally before starting vscode. See Configuration for details.
One of the strengths of vscode is the use of well-documented configuration files. You can find comprehensive documentation for these online.
However, setting these up is time-consuming so the build system can create them for you. The vscode workspace root directory is your project directory.
Change to your project directory (e.g. samples/Basic_Blink) and run these commands:
make ide-vscode SMING_ARCH=Esp8266
make ide-vscode SMING_ARCH=Host
Now open the workspace in vscode, and open a source file (.c, .cpp, .h). You should now be able to select the architecture from the icon in the bottom-right corner:
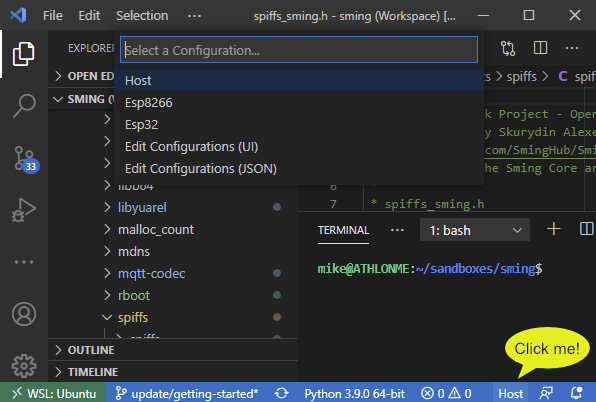
VS Code language selection
A selection of tasks are provided which you can view via Terminal -> Run Task.
To debug your application, follow these steps:
Select the appropriate architecture (e.g. Host, Esp8266)
Select
Terminal->Run Task->Full rebuild (with debugging)Confirm that the baud rate (
COM_SPEED_GDB) and port (COM_PORT_GDB) are set correctly:make gdb SMING_ARCH=Esp8266 COM_PORT_GDB=/dev/ttyUSB0 COM_SPEED_GDB=115200
Update the vscode configuration:
make ide-vscodeIn vscode, select the require ‘Run’ task:
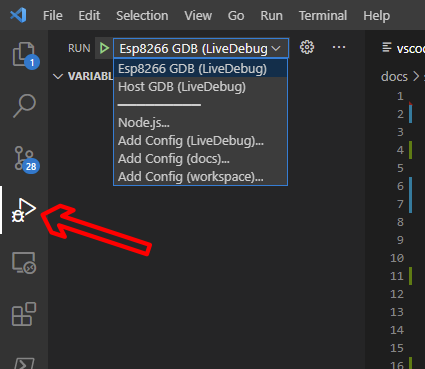
VS Code debug selection
Manual configuration changes
When you run make ide-vscode the configuration files are actually generated using a python script
Tools/vscode/setup.py. Configuration variables are passed from the project makefile.
If you make any changes to the configuration files, please note the following behaviour:
The
Host,Esp32orEsp8266intellisense settings will be overwritten.The
Esp8266 GDBandHost GDBlaunch configurations will be overwrittenThe
sming.code-workspaceand.vscode/tasks.jsonfiles will be created if they do not already exist. To re-create these they must first be deleted.
Ideally the vscode configuration files should not need to be kept under configuration control, but generated when required.
Some settings are necessarily configured via the setup.py script, however most settings can
be changed by editing the files in Tools/vscode/template.
If you do this, remember to keep a copy as they’ll be overwritten otherwise.
And, please consider contributing any changes or suggestions to the community!
Known issues / features
The vscode configuration files are only updated when you manually run
make ide-vscode. If you update change critical build variables or add/remove Components to your project, you may need to run it again to update them.When running
make ide-vscode, comments in the configuration files will be discarded.make ide-vscodemay overwrite parts of your configuration: be warned!When debugging for esp8266 output in the console is not formatted correctly. Lines appear with @ in front of them.
You may find vscode uses powershell instead of cmd.exe to execute tasks. Sming should work OK with either, but you can change this in the sming.code-workspace file via the
terminal.integrated.defaultProfile.windowssetting.